Material handling systems fail quietly before they fail. A conveyor may still run, but uneven belt tracking, excess vibration, and premature wear begin to slow operations. These issues often trace back to one overlooked component: idler rollers.
Selecting incorrect idler conveyor rollers increases maintenance costs, shortens belt life, and disrupts production schedules. For businesses across the United States that rely on conveyor belts to move materials efficiently, understanding idler roller types is critical. The right selection supports stable operation, consistent load handling, and predictable performance.
Why Idler Roller Selection Matters
Idler rollers support the conveyor belt and guide material flow. When rollers do not match load requirements or belt design, issues quickly arise.
Poor selection often leads to:
- Uneven belt tracking
- Increased belt tension
- Premature bearing wear
- Higher energy consumption
- Frequent unplanned downtime
Choosing the correct idler conveyor roller type reduces friction, stabilizes belt movement, and protects long-term system reliability.
What Are Idler Conveyor Rollers?
Idler conveyor rollers are cylindrical components mounted along the conveyor frame. They support the belt and the conveyed material while maintaining alignment and smooth motion.
Idler rollers do not drive the belt. Instead, they manage load distribution, belt sag, and directional stability. Their design varies based on load weight, belt width, material type, and operating environment.
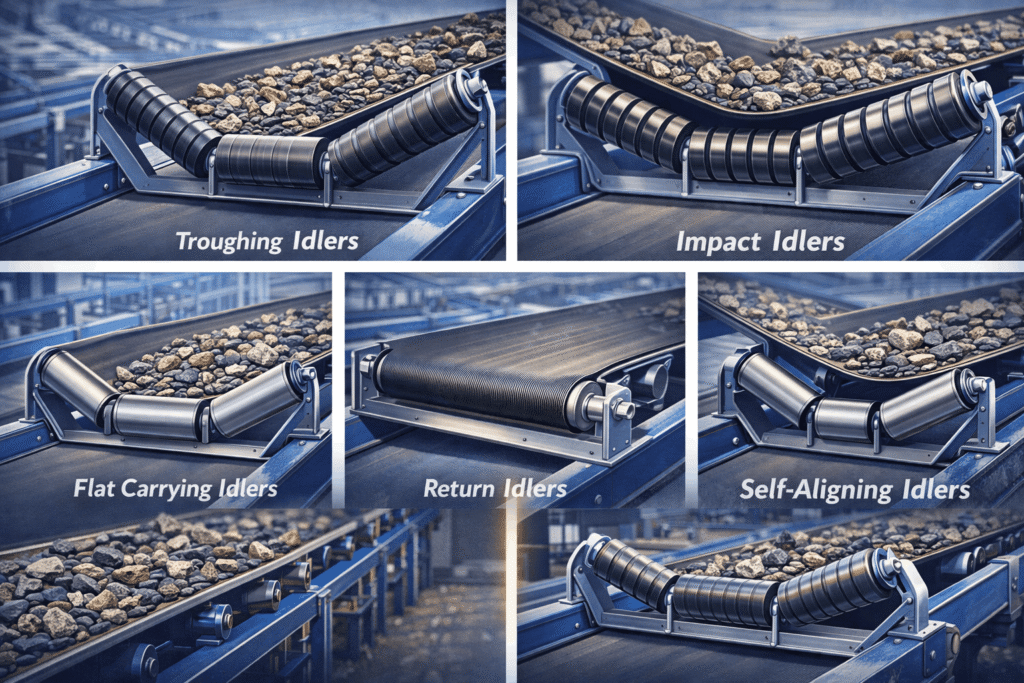
Common Conveyor Idler Roller Types
Each idler roller type serves a specific function within a conveyor system. Selecting the correct type ensures balanced performance across the entire line.
1. Carrying Idler Rollers
Carrying idlers sit on the load-carrying side of the belt. They support the material’s weight and maintain the belt’s shape.
Key characteristics:
- Positioned along the upper belt run
- Designed for continuous load support
- Available in various diameters and spacing
2. Return Idler Rollers
Return idlers support the belt on the return path after material discharge. Their role focuses on belt alignment and minimizing sag.
Key characteristics:
- Installed on the return side of the custom conveyor roller
- Reduce belt drag and wear
- Often spaced farther apart than carrying idlers
3. Troughing Idler Rollers
Troughing idlers use angled rollers to form a trough shape. This configuration increases load capacity while keeping material centered.
Key characteristics:
- Typically arranged in three-roller sets
- Improve material containment
- Common in bulk material handling
4. Impact Idler Rollers
Impact idlers protect the belt at material transfer zones. They absorb impact energy from falling materials.
Key characteristics:
- Equipped with rubber rings or cushioned surfaces
- Installed at loading and transfer areas
- Extend the belt and heavy-duty conveyor roller lifespan
5. Training Idler Rollers
Training idlers help keep the belt centered during operation. They pivot slightly to correct tracking issues.
Key characteristics:
- Automatically adjust belt alignment
- Reduce edge wear
- Support consistent conveyor performance
How to Choose the Right Idler Roller Type
Effective selection begins with understanding operating conditions rather than relying on default configurations.
Consider the following factors:
- Material weight and density
- Belt width and speed
- Conveyor length and layout
- Loading and transfer points
- Environmental conditions
Matching idler roller design to these variables ensures stable performance and controlled wear.
Common Idler Roller Selection Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced operations teams encounter avoidable issues when selecting material handling rollers.
Common mistakes include:
- Using standard idlers at high-impact zones
- Incorrect roller spacing for load conditions
- Ignoring belt speed and tension requirements
- Overlooking environmental exposure
Avoiding these mistakes reduces long-term maintenance costs and protects conveyor uptime.
Building a Reliable Conveyor System Starts With the Right Idlers
Reliable conveyor performance begins with the correct selection of idler rollers. Understanding idler types and their roles helps businesses reduce downtime and extend system lifespan.
Conveyor reliability depends on thoughtful component selection. Idler rollers influence belt life, tracking accuracy, and energy efficiency across the entire system.
Selecting idler rollers based on operating demands supports consistent material flow and reduces unexpected disruptions. Businesses planning upgrades or replacements benefit from reviewing idler configurations with trusted conveyor rollers suppliers.